Collagen, Cholesterol, and the Tunica Intima: The Link and Its Implications
Summary of the Article:
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Importance of Collagen in Health | Collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity |
| Impact of Collagen on Cholesterol | Collagen aids in reducing LDL cholesterol levels in the bloodstream |
| Connection Between Collagen and the Tunica Intima | Collagen contributes to the structural integrity of the tunica intima |
| Role of Vitamin C in Collagen Synthesis | Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis in the body |
| Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Collagen | Certain lifestyle habits, like smoking and sun exposure, can degrade collagen |
| Benefits of Collagen Supplementation | Collagen supplements can improve skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles |
| Dietary Sources of Collagen | Foods like bone broth, fish, and chicken skin are rich in collagen |
| Is Carbon 60 the Ultimate Antioxidant | Carbon 60, as the most powerfull antioxydant can help your blood vessels |
Introduction
Cholesterol, often the talk of the town at family dinners, is a key player in your body's health. But did you know it's also connected to collagen and the tunica intima? In this article, we'll unravel this mystery, and you'll learn how these connections impact your vascular well-being. So, sit back and let us be your cholesterol whisperer, guiding you through a journey of health, antioxidants, and blood vessels!
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Effects on the Body
LDL Cholesterol and Atherosclerosis
Cholesterol is a type of fat that circulates in the bloodstream. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis when it builds up in the artery walls. Atherosclerosis is the process in which plaque forms in the blood vessels, leading to decreased blood flow and increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Good Blood Pressure vs High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries. Good blood pressure is essential for maintaining healthy blood flow and preventing damage to the blood vessels. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can strain the blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
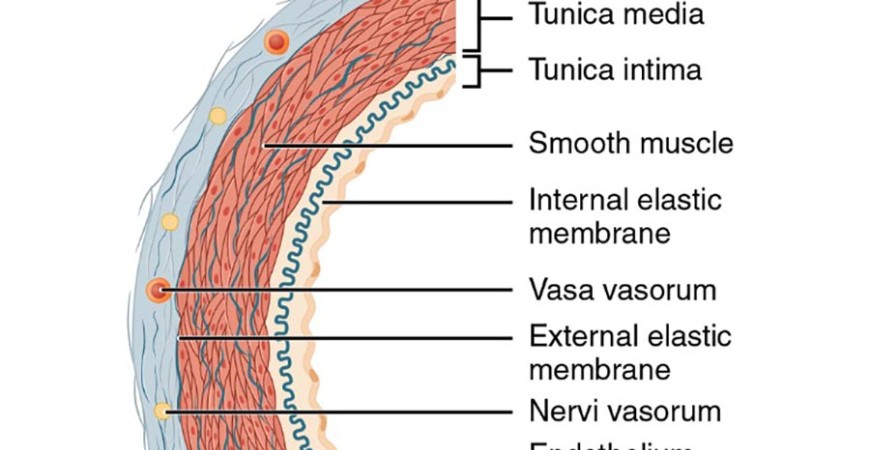
The Role of Collagen in the Tunica Intima
Structure and Function
The tunica intima is the innermost layer of blood vessels, composed mainly of collagen and endothelial cells. Collagen provides structural support and maintains the elasticity of blood vessels, allowing them to expand and contract to accommodate blood flow.
Connection to Atherosclerosis
Collagen degradation and loss of elasticity in the tunica intima can lead to plaque formation and contribute to atherosclerosis. When collagen is damaged, the blood vessel walls become more susceptible to inflammation, oxidative stress, and LDL cholesterol infiltration.
Inflammation and Its Effects on Collagen and Cholesterol
Chronic Inflammation and Vascular Health
Chronic inflammation can harm collagen and cholesterol, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis. Inflammation can produce free radicals, which damage collagen and contribute to LDL cholesterol oxidation. Oxidized LDL cholesterol is more likely to accumulate in the blood vessel walls, forming plaque.
Peripheral Artery Disease Symptoms
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when blood vessels in the limbs narrow due to atherosclerosis. Symptoms of PAD can include leg pain while walking, numbness, and coldness in the affected limbs. Chronic inflammation can exacerbate PAD symptoms by further damaging collagen and contributing to atherosclerosis progression.
Antioxidants in the Battle Against Free Radicals and Aging
The Importance of Glutathione
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that is crucial in neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative stress. By protecting collagen from damage and reducing the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, glutathione can help maintain vascular health and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
Flavonols as Antioxidant Agents
Flavonols are a group of plant-based compounds that have antioxidant properties. They can help combat free radicals, protect collagen from damage, and inhibit LDL cholesterol oxidation. A diet rich in flavonol-containing foods, such as berries, onions, and green tea, may help improve vascular health and prevent atherosclerosis.
The Connection Between Mitochondria and Cholesterol Metabolism
Mitochondria's Role in Cellular Health
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells, responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). They are critical in maintaining cellular health and function, including cholesterol metabolism and synthesis.
The Impact on Blood Pressure
Mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to imbalances in cholesterol metabolism and contribute to the development of high blood pressure. By improving mitochondrial function through lifestyle changes and consuming antioxidant-rich foods, one can lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
Strategies to Lower Cholesterol and Improve Vascular Health
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Diet and lifestyle changes can significantly impact cholesterol levels and vascular health. A diet rich in fibre, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking can contribute to better vascular health.
The Benefits of Maintaining a Low Blood Pressure Range
Maintaining a low blood pressure range can help reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. Adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing stress can effectively lower blood pressure and improve overall vascular health.
Carbon 60: The Ultimate Antioxidant for Rejuvenating Your Blood Vessels
Did you know that carbon 60 is a potent antioxidant and can also help synthesize collagen? Collagen is a vital component of our body that plays a crucial role in rebuilding the inner layer of our blood vessels, called the tunica intima. When the tunica intima is restored with collagen, cholesterol naturally disappears. Imagine the benefits of incorporating this extraordinary antioxidant into your routine! Are you ready to experience a healthier and more vibrant life? Take advantage of this opportunity to optimize your vascular health!
Conclusion
The connection between collagen, cholesterol, and the tunica intima is crucial for understanding vascular health. Chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction can contribute to atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, consuming antioxidant-rich foods, and maintaining good blood pressure, individuals can improve their vascular health and reduce the risk of serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do antioxidants help in reducing inflammation and cholesterol levels?
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative stress, which can damage collagen and contribute to the oxidation of LDL cholesterol. By protecting collagen and reducing LDL cholesterol oxidation, antioxidants can help maintain vascular health and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
2. Can dietary changes alone effectively lower cholesterol and improve vascular health?
Nutritional changes can significantly impact cholesterol levels and vascular health. However, combining diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors is most effective for achieving optimal vascular health.
3. What are the potential consequences of ignoring high cholesterol levels?
Ignoring high cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
4. How can chronic inflammation affect one's overall health?
Chronic inflammation can damage collagen and contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases. It has also been linked to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
5. What are the most effective natural sources of antioxidants?
Some of the most effective natural sources of antioxidants include fruits (especially berries), vegetables (such as leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables), nuts, seeds, and beverages like green tea and red wine. A varied diet rich in these antioxidant-rich foods can help protect against oxidative stress and support overall health.
6. How does Carbon 60 (C60) interact with cholesterol in the body?
Research indicates that C60 may affect cholesterol levels due to its properties as a potent antioxidant. Studies show that C60 can interact with lipid bilayers, potentially influencing cholesterol's behavior and its translocation across these layers, which might impact overall cholesterol management. However, further studies are needed to fully understand its effects and safety in humans.
7. What is collagen and why is it important for the tunica intima?
Collagen plays a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of the tunica intima, the innermost layer of blood vessels, by providing necessary strength and flexibility.
8. How does cholesterol affect the tunica intima?
Excessive cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the tunica intima, contributing to atherosclerosis and potentially leading to cardiovascular diseases.
9. What is the tunica intima and its function in the cardiovascular system?
The tunica intima is the inner layer of the artery that is involved in nutrient exchange and blood flow regulation within the cardiovascular system.
10. Can improving collagen levels in the body help with cholesterol management?
Increasing healthy collagen production might indirectly affect cholesterol by maintaining the integrity of the tunica intima, potentially reducing plaque formation.
11. What are the sources of collagen for improving tunica intima health?
Dietary sources like bone broth, marine collagen, chicken, and leafy greens can boost collagen levels, supporting tunica intima health.
12. What lifestyle changes can affect both collagen and cholesterol levels positively?
Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, and avoiding smoking can improve both collagen production and cholesterol levels.
13. How does aging affect collagen, cholesterol, and the health of the tunica intima?
Aging can decrease natural collagen production and worsen cholesterol profiles, which might compromise the health of the tunica intima.
14. What are the symptoms of tunica intima damage?
Symptoms may include reduced elasticity in blood vessels, higher blood pressure, and increased risk of cardiovascular events.
15. What preventive measures can be taken to protect the tunica intima from damage?
Maintaining a healthy diet, regular cardiovascular exercise, and monitoring blood cholesterol levels are key preventive measures.
Sources
- PubMed - The effect of C60 fullerene on the mechanokinetics
- Healthline - Carbon 60 (C60): How to Take, Where to Buy, and More
- ResearchGate - Determination of the Sputtering Yield of Cholesterol Using
- Cleveland Clinic - Cholesterol: Understanding Levels and Numbers
- Mayo Clinic - Cholesterol level: Can it be too low?
- PubMed - Cholesterol affects C₆₀ translocation across lipid bilayers