Explore the Benefits of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) for Anti-Aging: Dosage, Research
Summary of this article:
| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| Why we need NMN | NMN is a NAD+ precursor that can help improve cellular function and increase NAD+ levels, potentially slowing down the aging process. It has minimal side effects and is well-tolerated. |
| What is NMN | NMN is a molecule crucial for energy metabolism in the human body. It's derived from niacin and plays a role in cellular biochemical functions. Research on its role in anti-aging and cancer management is ongoing. |
| Foods containing NMN | Broccoli, Cabbages, Edamame, Mushroom, Tomatoes, Avocado, Cucumber, Shrimp, Raw Beef |
| Benefits of NMN | NMN can slow down aging, improve memory and cognitive function, treat type II diabetes, protect the brain from damage, improve metabolism, and uphold youthfulness. |
| NMN Vs NR | NMN and NR are both precursors of NAD+. NMN has a larger molecular size and is typically more expensive than NR. |
| NMN Research | Research on NMN has focused on its potential anti-aging properties, improved cardiovascular health, bolstered physiological and immunological functions, and potential neurodegenerative benefits. |
| NMN Dosage | The recommended dosage of NMN varies, but the general range is typically between 250mg to 500mg daily. |
| Is NMN safe? | Current research suggests that NMN is safe to use. Clinical trials on NMN have not reported any serious side effects. |
| NMN Supplement | NMN can be taken as a dietary supplement. It's recommended to take NMN in sublingual form (under the tongue) rather than oral tablets. |
Why we need Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN)
As we age, our bodies go through a series of changes that can lead to a decline in overall health and well-being. But what if there was a way to slow down or even reverse the aging process? Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) may hold the key to living a longer, healthier life.
NMN is a NAD+ precursor, a crucial biomarker in human cells. As we age, NAD+ levels decline due to enzymatic functions. However, supplementing with NMN can help to improve cellular function and increase NAD+ levels, potentially slowing down the aging process.
But what sets NMN apart from other anti-aging treatments? Unlike many other options, NMN has minimal side effects and is well-tolerated. Learn more about the potential of NMN for anti-aging and how it can improve your lifespan."
What is Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN)
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a molecule that plays a crucial role in the human body's energy metabolism. It is derived from niacin and is a product of the reaction between nicotinamide ribose and a phosphate group. NMN is a substrate for the enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase, which converts it to NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a fundamental molecule in cellular biochemical functions.
Recent preclinical studies have shown that NMN may have therapeutic potential in reversing the aging process and managing cancer. As a precursor of NAD+, a decline in NMN levels can have a drastic effect on overall health. The research on NMN's role in anti-aging and cancer management is promising and ongoing.
What foods contain Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN)
Broccoli, Cabbages, Edamame, Mushroom, Tomatoes, Avocado, Cucumber, Shrimp, Raw Beef
What are the benefits of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN)
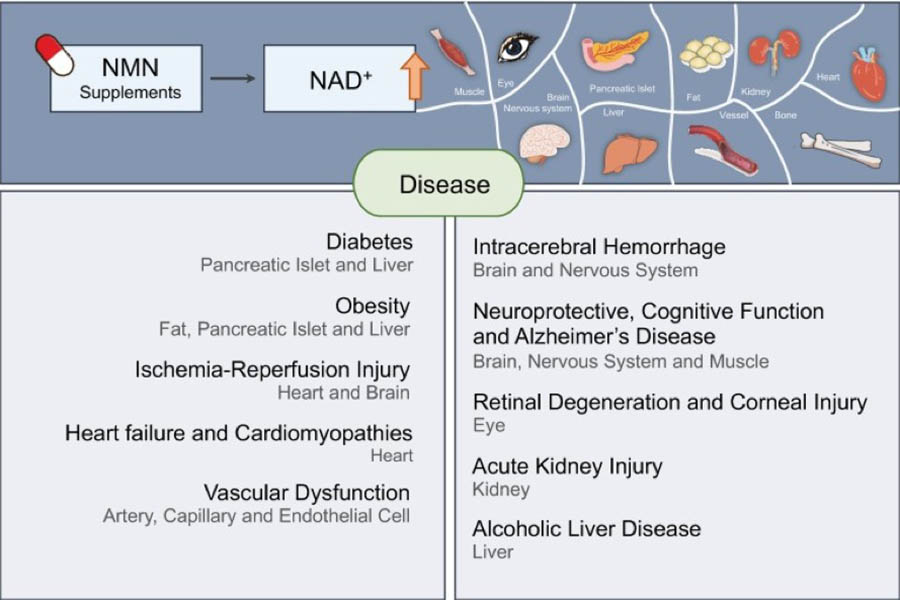
- Anti-Aging Supplement: Research by Dr. David Sinclair of Havard University has confirmed the efficiency of NMN in slowing down aging. This can improve memory and cognitive function. The decline in NAD+ levels as we age can lead to a decline in energy production by the mitochondria. NMN can help to increase NAD+ levels in the body and activate sirtuins, which are enzymes that play a crucial role in aging and longevity. By improving cellular function, NMN can help to slow down the aging process and improve overall health and wellness.
- Treatment of Diabetes II: NMN can improve glucose intolerance and insulin sensitivity in patients with diabetes. A decline in NAD+ levels can trigger type II diabetes. By administering NMN, it can significantly improve glucose intolerance and insulin sensitivity in patients with diabetes. Additionally, some geneticists inferred that the treatment reverses the gene expression that’s due to a high-fat diet.
- Neuroprotection: NMN can protect the brain from damage and improve cognitive function, making it a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's syndrome, and dementia. When NAD+ levels fall, the mental state lies at stake. Administering NMN optimizes the quantity of NAD+, hence protecting the brain from damage. It can improve neuronal functions and cognition, including, learning, and memory.
- Improved Metabolism: Optimal NMN levels in the body can increase NAD+ and improve metabolism, potentially helping with weight loss and reducing the risk of obesity, diabetes, fatty liver, and dyslipidemia. NAD+ regulates energy metabolic functions, repair of DNA, and response to stress. NMN directly affects metabolism and its deficiency would trigger several metabolic conditions. In the case of glucose intolerance, NMN steps in to enhance the metabolism of sugar. Research confirms that you can lose up to 10% of your bodyweight if you take NMN.
- Upholding Youthfulness: NMN, a compound, can undo the wear and tear in blood vessels, thus decelerating the aging process. NMN can enhance blood flow and muscle endurance while reversing vascular atrophy and senescence. The key ingredient that makes all this possible is SIRT1, a protein that regulates multiple metabolic pathways. If there is a decrease in the level of SIRT1 in human endothelial cells, blood flow diminishes significantly. However, by supplementing NMN, sirtuin-signaling is activated, and this triggers the development of new capillaries that provide oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and other vital organs. This leads to a reduction in the aging process, an improvement in muscle endurance, and an overall enhancement of health and well-being.
NMN Vs NR
Regarding precursors of NAD+ - a molecule that plays a critical role in various cellular functions - two compounds that come to mind are Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and riboside. Although both these molecules are related, some key differences are worth noting.
One of the main differences between the two is their molecular size. Specifically, NMN has a larger molecular size than riboside, meaning it cannot pass through the human body easily without breaking down into its constituent parts. However, scientists have recently discovered a transporter called Scl12a8 protein that can facilitate the conversion of NMN to NAD+.
Another difference between these two precursors is their cost. Typically, NMN is more expensive than riboside. However, it's worth noting that further research is needed better to understand the differences and benefits of these compounds.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN) Research
Since its discovery back in 1963, Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has garnered a lot of attention in the scientific community. Researchers have been exploring the various potential benefits that this molecule may offer, including anti-aging properties, improved cardiovascular health, bolstered physiological and immunological functions, and even potential neurodegenerative benefits. Let's take a closer look at some of the research studies that have focused on NMN:
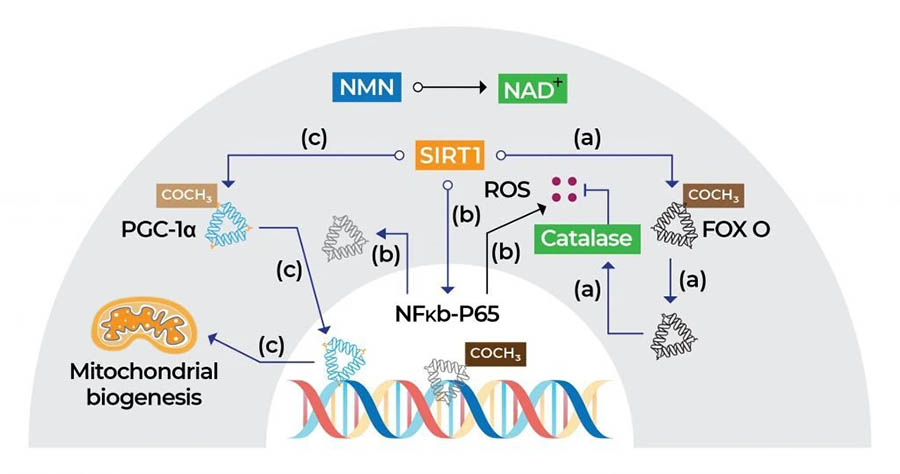
- Anti-Aging: In 2013, Dr. David Sinclair from Harvard University found that NMN can improve muscle capacity and metabolism in mice models. He also found that it was as effective as working out, and did not have any side effects.
- Cardiovascular Health: In 2014, Yamamoto and his associates found that NMN has cardio-protective properties, and can protect the heart from reperfusion and ischemic injury. In 2016, De Picciotto and his team found that it can also promote vascular functionality.
- Neurodegeneration: In 2015, Long and his team found that NMN can treat Alzheimer's disease and reduce its symptoms. In 2016, Wang and his team found that it can also counter cognitive disorders and neural impairment.
- Physiological and Immunological Functions: In 2013, Mills and his team found that NMN can manage type II diabetes. In 2016, he found that it can also counter physiological and immunological decline in old mice, and reduce oxidative stress.
- Mysterious Transporter: In recent years, Imai and his team discovered a protein called Slc12a8 that aids in the assimilation of NMN into the body, which can increase its bioavailability.
- Clinical Trials: Since 2017, Scholars from Keio University in Tokyo and Washington University have been conducting clinical trials on NMN among aged but healthy subjects. The aim is to establish the safety of the supplement and understand how it affects beta-cell functions and if there are any side effects.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN) Dosage
Determining the appropriate amount of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation can be a common query for many individuals. While recommended dosages may vary based on the source, the general range is typically between 250mg to 500mg daily.
In clinical trials, test subjects were given a maximum of 500mg of NMN daily. ON THE OTHER HAND, renowned NMN researcher David Sinclair takes approximately 900mg daily. Although some users have reported taking up to 1000mg daily, it's crucial to acknowledge that NMN has no known adverse effects.
Starting with the lowest dosage possible and gradually increasing it as needed is always recommended.
Is Nicotinamide Mononucleotide safe? A look at the current research
When it comes to the safety of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN), the current research suggests that it is safe to use. To date, there is no evidence to indicate that NMN is unsafe. In fact, clinical trials on NMN have not reported any serious side effects in the subjects. Additionally, preclinical studies on NMN have also been successful without reporting any adverse symptoms. However, it's always important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplement, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking any medications.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN) Supplement
As Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has not yet received full endorsement by the FDA, it cannot be prescribed as a drug. However, it can be taken as a dietary supplement. While you may be able to find it in local drug stores, the best place to purchase NMN is online from a reputable supplier. You can choose to buy NMN in bulk powder for research purposes or as a dietary supplement.
To enhance its bioavailability, it's recommended to take NMN in sublingual form (under the tongue) rather than oral tablets. According to FDA standards, a person needs a minimum of 560mg of NMN per day. While certain foods like broccoli and cabbage contain small amounts of NMN, it would be impossible to consume the large quantities necessary to meet the FDA requirements. Therefore, purchasing a supplement from a reputable supplier is the most practical option.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)?
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a molecule that plays a crucial role in the human body's energy metabolism. It is derived from niacin and is a product of the reaction between nicotinamide ribose and a phosphate group.
2. Why is NMN important for anti-aging?
NMN is a NAD+ precursor, a crucial biomarker in human cells. As we age, NAD+ levels decline, but supplementing with NMN can help to improve cellular function and increase NAD+ levels, potentially slowing down the aging process.
3. What foods contain NMN?
Foods that contain NMN include broccoli, cabbages, edamame, mushrooms, tomatoes, avocados, cucumbers, shrimp, and raw beef.
4. What are the benefits of NMN?
NMN has several potential benefits, including slowing down aging, improving memory and cognitive function, treating type II diabetes, protecting the brain from damage, improving metabolism, and upholding youthfulness.
5. What is the difference between NMN and NR?
NMN and NR are both precursors of NAD+. The main differences between the two are their molecular size and cost. NMN has a larger molecular size and is typically more expensive than NR.
6. What research has been done on NMN?
Research on NMN has focused on its potential anti-aging properties, improved cardiovascular health, bolstered physiological and immunological functions, and potential neurodegenerative benefits.
7. What is the recommended dosage of NMN?
The recommended dosage of NMN varies, but the general range is typically between 250mg to 500mg daily. However, some individuals, like renowned NMN researcher David Sinclair, take up to 750mg daily.
8. Is NMN safe to use?
Current research suggests that NMN is safe to use. Clinical trials on NMN have not reported any serious side effects.
9. Can NMN be prescribed as a drug?
As of now, NMN has not yet received full endorsement by the FDA, so it cannot be prescribed as a drug. However, it can be taken as a dietary supplement.
10. Where can I buy NMN?
While you may be able to find NMN in local drug stores, the best place to purchase NMN is online from a reputable supplier. You can choose to buy NMN in bulk powder for research purposes or as a dietary supplement.










